Databricks lakehouse federation allows you to run federated queries against external data sources directly from Databricks. This means you can connect your Databricks workspace to your Neon Postgres database and query it without needing to copy or move the data. This enables you to combine data from Neon with other data sources managed by Databricks and leverage the powerful analytics and governance capabilities of the Databricks lakehouse Platform.
This guide will walk you through setting up lakehouse federation to query data residing in your Neon Postgres database.
Why use lakehouse federation with Neon Postgres?
Lakehouse federation provides several benefits when integrating Neon Postgres with Databricks:
- Query data in place: Access and query your Neon Postgres data where it lives, eliminating the need for complex and time-consuming ETL processes to move data into Databricks. This ensures you're always working with the freshest data.
- Faster insights: Get to insights quicker by directly querying live data. This is ideal for ad hoc reporting, proof-of-concept work, and the exploratory phase of new data pipelines or reports.
- Unified governance: Manage access to your Neon data through Databricks Unity Catalog. This includes fine-grained access control (table and view-level permissions), data lineage to track how data is used, and auditing capabilities.
- Leverage external compute: For complex analytical workloads, you can use Databricks compute resources to run queries against your Neon Postgres data, taking advantage of Databricks' performance optimizations and scalability.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
Neon prerequisites
A source Neon project with a database containing the data you want to query. If you're just testing this out and need some data to play with, you run the following statements from the Neon SQL Editor or an SQL client such as psql to create a table with sample data:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS playing_with_neon(id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY, name TEXT NOT NULL, value REAL);
INSERT INTO playing_with_neon(name, value)
SELECT LEFT(md5(i::TEXT), 10), random() FROM generate_series(1, 10) s(i);To connect to your Neon Postgres database from Databricks, you'll need your connection details. You can find them in your Neon Project dashboard under Connection Details. Learn more: Connect from any application.
It's recommended that you create a dedicated Postgres role in Neon with the principle of least privilege (e.g.,
SELECTon specific tables/schemas) for use with Databricks.
Databricks prerequisites
- A Databricks workspace enabled for Unity Catalog.
- Compute requirements:
- Databricks clusters must use Databricks Runtime 13.3 LTS or above and be configured with Standard or Dedicated access mode.
- SQL warehouses must be Pro or Serverless and use version 2023.40 or above.
- Permissions required in Databricks:
- To create a connection: You must be a metastore admin or a user with the
CREATE CONNECTIONprivilege on the Unity Catalog metastore attached to the workspace. - To create a foreign catalog: You must have the
CREATE CATALOGpermission on the metastore and be either the owner of the connection or have theCREATE FOREIGN CATALOGprivilege on the connection.
- To create a connection: You must be a metastore admin or a user with the
Setting up lakehouse federation for Neon Postgres
Follow these steps to configure Databricks to query your Neon Postgres database.
Create a connection to Neon Postgres
A connection in Databricks allows you to define how to connect to an external data source like Neon Postgres. It stores the necessary details, such as the hostname, port, user credentials, and connection type. This connection can then be used to create a foreign catalog that mirrors your Neon database structure in Databricks.
You can create a connection using either Catalog Explorer or SQL.
- In your Databricks workspace, navigate to Catalog.
- In the Catalog Explorer, click the + Add Data button at the top of the left pane and select Create a connection.
- On the Set up connection wizard:
- Connection name: Enter a user-friendly name for your connection (e.g.,
neon_production_connection). - Connection type: Select
PostgreSQLfrom the dropdown. - (Optional) Comment: Add a description for the connection.
- Click Next.
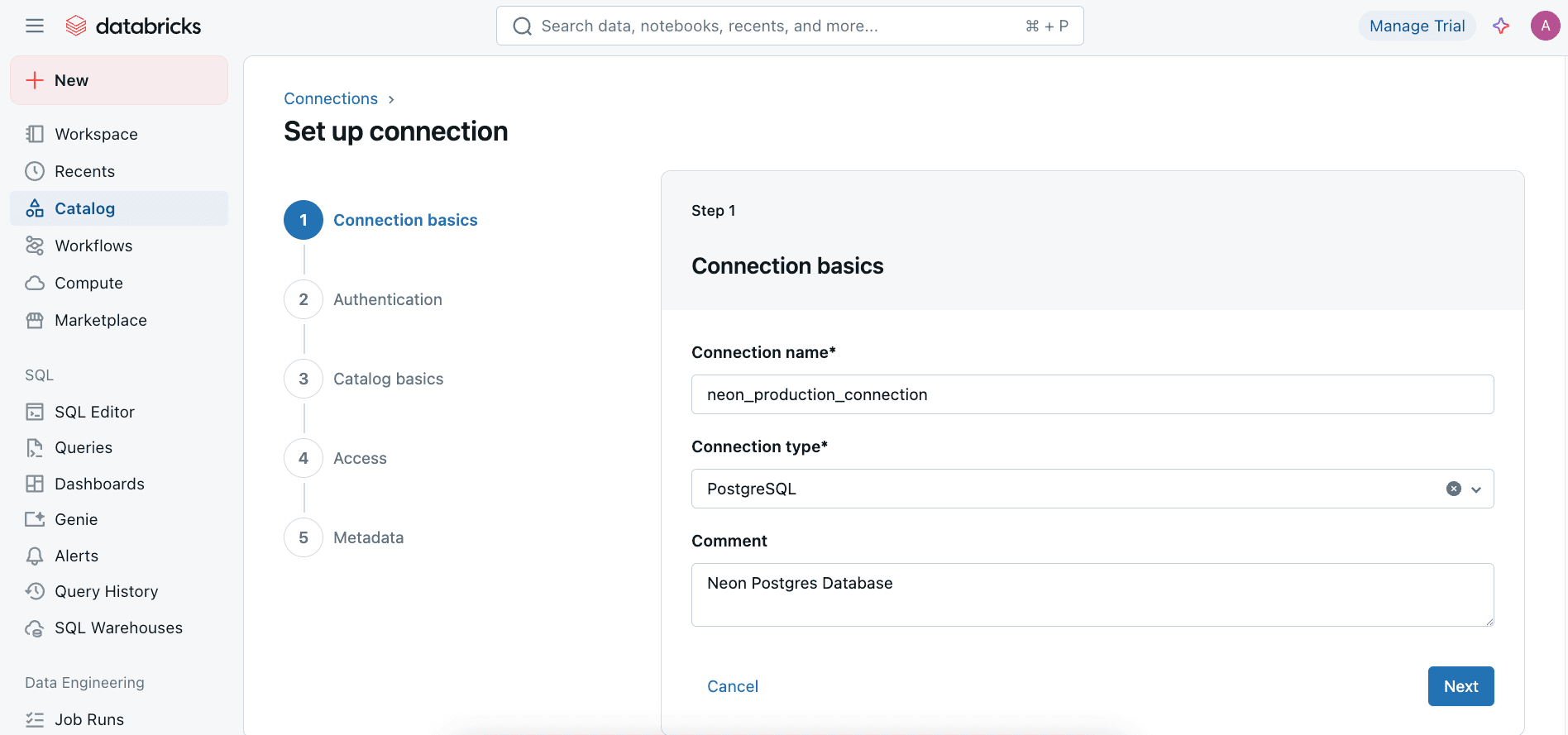
- Connection name: Enter a user-friendly name for your connection (e.g.,
- On the Authentication page, enter the connection properties for your Neon Postgres instance:
- Host: Your Neon Postgres hostname (e.g.,
ep-cool-darkness-123456.us-east-2.aws.neon.tech). - Port:
5432 - User: The Neon Postgres role
- Password: The password for the Neon Postgres role.
- Host: Your Neon Postgres hostname (e.g.,
- Click Create connection.
- On the Catalog Basics page, enter your Database name in Neon Postgres that you want to query (e.g.,
neondb,postgres, or your custom database name). - Click Test connection to verify the connection details. If successful, you will see a confirmation message.
- Click Create catalog to finalize the connection setup.
- On the Access page, select the workspaces in which users can access this connection and grant appropriate privileges. You can assing READ ONLY (Data Reader) or READ WRITE (Data Editor) access depending on your use case.
- (Optional) On the Metadata page, specify tags for the connection.
- Click Create connection.
Create a Foreign Catalog for your Neon Database
A foreign catalog in Unity Catalog mirrors the database structure (schemas and tables) from your Neon Postgres instance, making it accessible for querying within Databricks.
You can skip this step if you created the connection using the Catalog Explorer, as it automatically creates a foreign catalog for you. The catalog will be named <connection_name>_catalog, where <connection_name> is the name you provided when creating the connection (e.g., neon_production_connection_catalog).
Querying Neon Postgres from Databricks
Once the connection and foreign catalog are set up, you can query tables in your Neon Postgres database using the standard three-level namespace: <foreign_catalog_name>.<schema_name>.<table_name>.
If you are following the playing_with_neon example from the prerequisites, you can run the following SQL query in the Databricks SQL editor:
SELECT *
FROM neon_production_connection_catalog.public.playing_with_neon;Here,
neon_production_connection_catalogis the foreign catalog created for your Neon Postgres connection.publicis the schema, andplaying_with_neonis the table. You'll need to replace these with your actual catalog, schema, and table names.
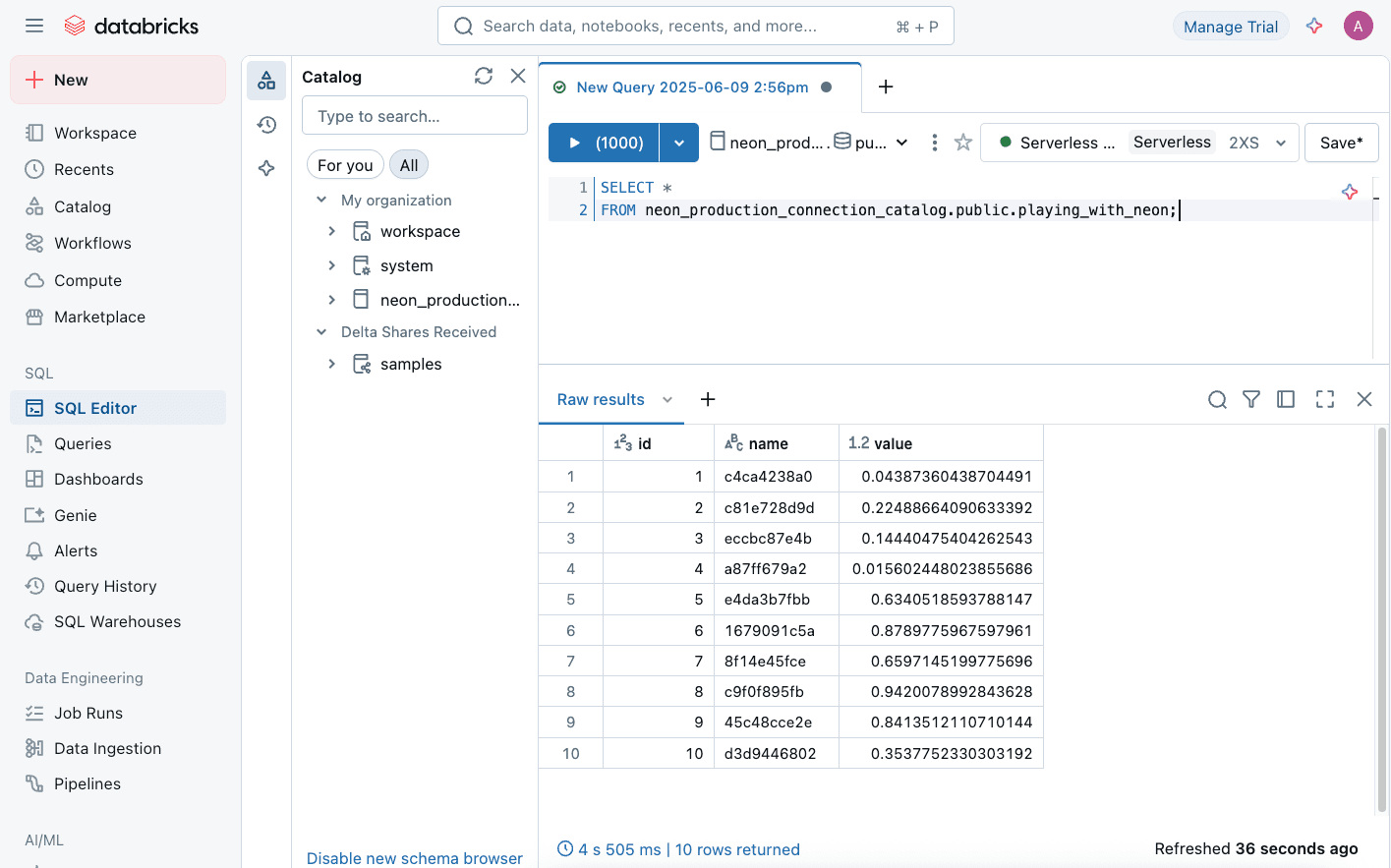
Databricks will translate this SQL statement into a query that runs against your Neon Postgres database, fetching the results directly into your Databricks environment.
Viewing system generated federated queries
To understand how Databricks translates your queries for the federated source, you can run an EXPLAIN FORMATTED SQL statement for your query.
EXPLAIN FORMATTED
SELECT *
FROM neon_production_connection_catalog.public.playing_with_neon
WHERE value > 0.5;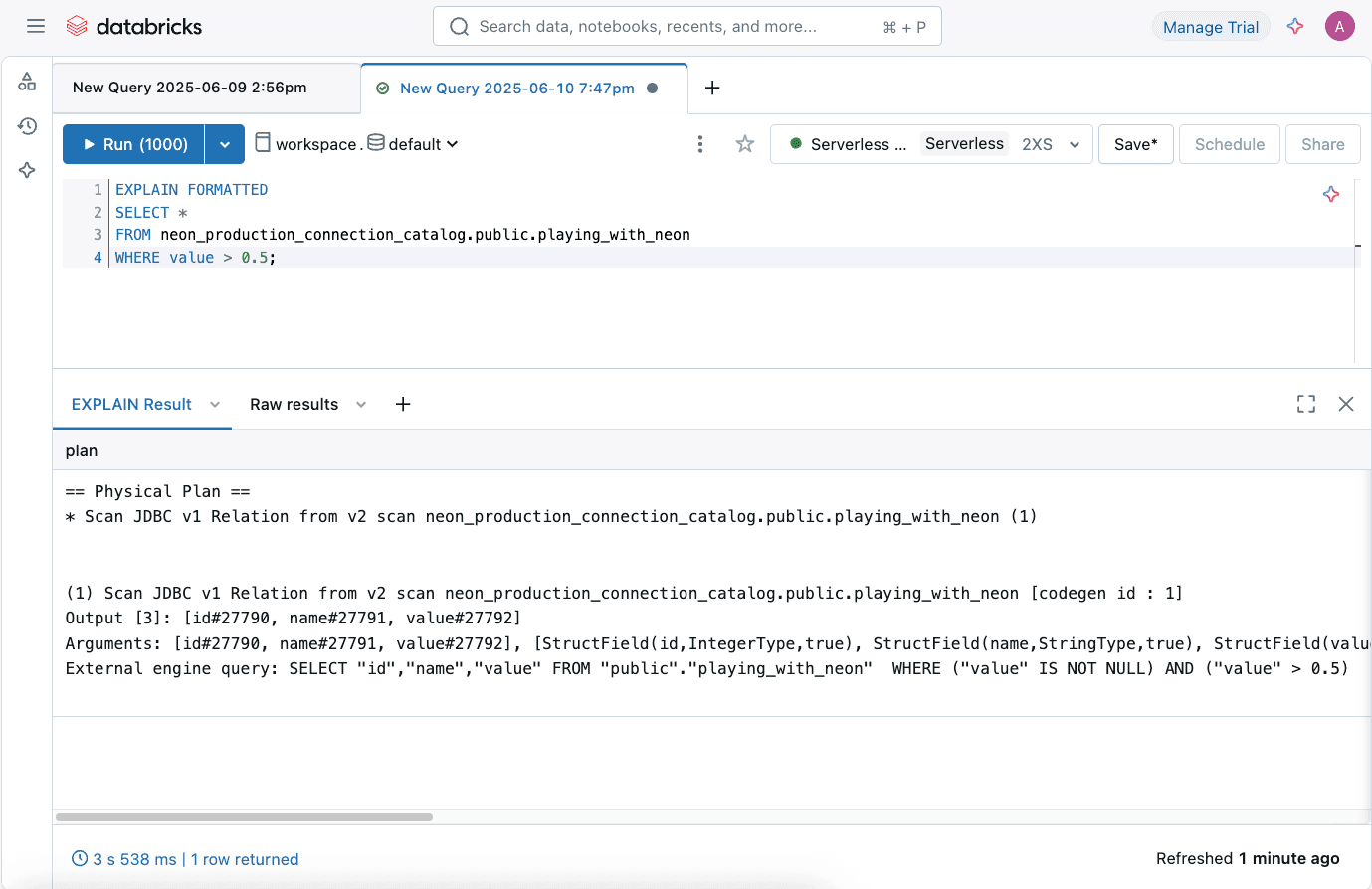
This helps in understanding what parts of the query are pushed down to Neon Postgres for execution.
Data type mappings
When you read data from Neon Postgres into Databricks Spark, data types are mapped as follows. This is important for understanding how your Neon data will be represented in Databricks.
| Postgres Type | Spark Type |
|---|---|
numeric | DecimalType |
int2 | ShortType |
int4 (if not signed) | IntegerType |
int8, oid, xid, int4 (if signed) | LongType |
float4 | FloatType |
double precision, float8 | DoubleType |
char | CharType |
name, varchar, tid | VarcharType |
bpchar, character varying, json, money, point, super, text | StringType |
bytea, geometry, varbyte | BinaryType |
bit, bool | BooleanType |
date | DateType |
tabstime, time, time with time zone, timetz, time without time zone, timestamp with time zone, timestamp, timestamptz, timestamp without time zone* | TimestampType/TimestampNTZType |
Postgresql array type** | ArrayType |
When you read from Postgres, Postgres Timestamp is mapped to Spark TimestampType if preferTimestampNTZ = false (default). Postgres Timestamp is mapped to TimestampNTZType if preferTimestampNTZ = true.
Limited array types are supported.
Supported pushdowns for Postgres
Refer to the Databricks Lakehouse Federation - Supported pushdowns for up-to-date information on the supported pushdowns for Postgres sources like Neon.
Best practices
- Dedicated Neon role: Create a dedicated Postgres role in Neon with the principle of least privilege (e.g.,
SELECTon specific tables/schemas). - Secure credentials: Always use Databricks secrets for storing Neon database credentials.
- Network configuration: Ensure your network allows connectivity from Databricks compute to your Neon endpoint. Review Neon's IP Allow settings to allow access from Databricks.
- Query optimization: Use
WHEREclauses to filter data as much as possible at the source (Neon) to minimize data transfer and improve query performance. Understand which operations can be pushed down. - Monitor usage: Regularly monitor query performance and resource usage on both Databricks and your Neon instance.
Conclusion
Databricks lakehouse federation provides a powerful and seamless way to query your Neon Postgres data directly, without data movement. By integrating Neon into your Databricks environment, you can unlock new insights, streamline your data workflows, and leverage the advanced analytics capabilities of the Databricks platform.
References
- Databricks Lakehouse Federation Documentation
- Databricks - Connect to PostgreSQL using Lakehouse Federation
- Databricks Unity Catalog Documentation
- Databricks Secrets Documentation
- Neon Documentation
Need help?
Join our Discord Server to ask questions or see what others are doing with Neon. Users on paid plans can open a support ticket from the console. For more details, see Getting Support.